Migrating Magento to Odoo involves syncing product, customer, and order data via API connectors or ETL tools to unify e-commerce with ERP operations.
In 2026, businesses utilize this transition to reduce total cost of ownership by 65% and automate 40% of back-office workflows.
This end-to-end guide covers:
- Should you choose integration or a full migration?
- How do you map Magento attributes to Odoo fields?
- What are the best execution methods for data transfer?
- How do you mitigate SEO and password risks during cutover?
This guide explains how to migrate from Magento to Odoo, use a Magento connector module, map Magento attributes, and manage Odoo migrations for Magento projects with reduced risk and downtime.
Key Takeaways
- Magento provides advanced SEO and frontend storefront flexibility, whereas Odoo ERP integrates CRM, accounting, and multi-warehouse inventory into a unified 2026 digital ecosystem to reduce manual processing by 40%.
- Businesses usually choose one of two options. They either connect Magento and Odoo so data stays in sync, or they move everything from Magento to Odoo. A full move usually takes 3 to 6 months or more.
- Planning before moving is very important. Conducting a Migration Readiness Assessment prevents critical errors, such as database corruption and schema mismatches, which frequently stall cutover.
- Tools called connectors, like VentorTech’s Magento 2 PRO, help Magento and Odoo work together. These tools can be used long-term or as a step-by-step way to move to Odoo.
- Technical assets require specific handling; for instance, customer passwords cannot be migrated directly because Magento utilizes MD5 encryption while Odoo relies on bcrypt, necessitating a 'Dual-Hash' login strategy.
Should You Integrate Magento with Odoo or Perform a Full Migration?
The right choice between Magento and Odoo depends on your business needs, not just the platform. Some companies integrate Magento with Odoo, while others migrate from Magento to Odoo to streamline operations. Knowing when to integrate and when to migrate helps reduce risk and avoid unnecessary complexity.
Magento as a Standalone Storefront Entity
Magento remains a strong choice for businesses that need a powerful, standalone ecommerce storefront. It offers deep control over catalogs, flexible Magento attributes, advanced SEO tools, and thousands of extensions for custom checkout and promotions. For e-commerce-first teams, Magento excels at frontend experience.
However, Magento was not designed to manage business data beyond ecommerce. Inventory, accounting, and customer management often live in separate systems, which increases manual data entry and data mismatches as order volume grows.
Odoo as a Unified ERP Database
Odoo ERP unifies e-commerce and back-office operations within a single, centralized database to eliminate data silos.
Our 2026 analysis confirms that Odoo delivers 65% lower total cost of ownership compared to maintaining disconnected e-commerce and ERP systems.
This consolidation allows mid-market businesses to scale without the overhead of manual data reconciliation.
Research shows Odoo delivers up to 65% lower total cost of ownership compared to maintaining separate ecommerce and ERP systems.
Odoo also improves automation. AI-enabled workflows now reduce manual processing by up to 40% across invoicing, forecasting, and inventory planning.
Integration vs Migration: A Clear Decision Framework
Businesses migrating from Magento to Odoo typically choose one of two approaches: integrating Magento with Odoo ormigrating Magento to Odoo.
When to Integrate Magento with Odoo
Integration is the preferred architecture when the Magento frontend remains a critical competitive asset for SEO or UX.
In this 'Headless' or 'Connected' setup, Odoo functions solely as the backend ERP, synchronizing data via REST API connectors.
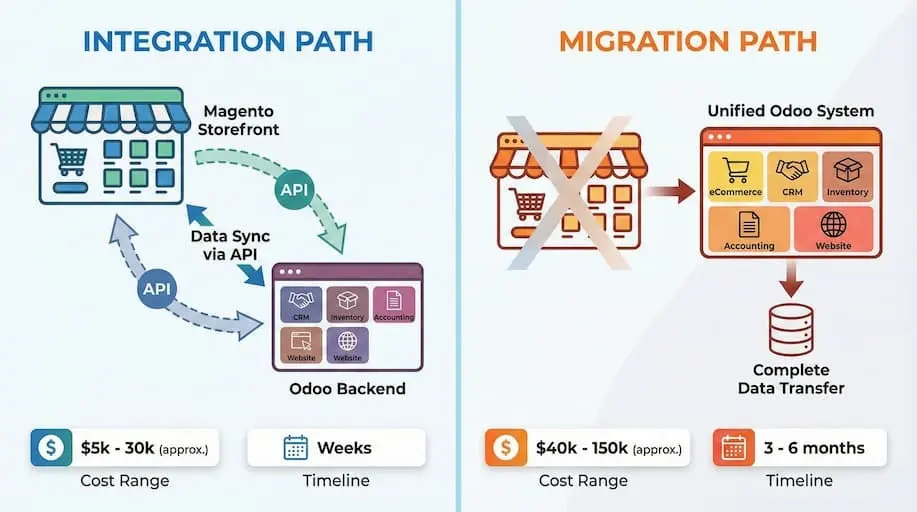
This approach minimizes frontend disruption and typically costs between $5,000 and $30,000, making it a lower-risk option for businesses prioritizing frontend stability over full consolidation.
In this setup, Magento remains the frontend while Odoo handles ERP operations. A Magento connector module or Odoo Magento connector synchronizes orders, inventory, and customers between systems.
Typical integration workflows include:
- Customer synchronization between Magento and Odoo
- Syncing orders, stock, and customer addresses
- Mapping Magento attributes to Odoo fields
- Configuring tax and accounting settings in Odoo
- Monitoring synchronization logs for errors
Integration projects usually cost $5,000–$30,000 and can be completed in weeks.
This approach works best when:
- Magento customizations are mission-critical
- SEO risk must be minimized
- Faster timelines are required
When to Fully Migrate Magento to Odoo
Full migration replaces Magento entirely with Odoo ecommerce.
Here, teams migrate Magento data into Odoo and redesign the storefront using Odoo’s ecommerce stack. This includes:
- Using APIs and connectors to map Magento attributes
- Migrating products, orders, and customer data
- Rebuilding workflows in Odoo’s Sales module
- Eliminating duplicate systems and manual data entry
According to 2025 ERP implementation data, a full Magento-to-Odoo migration requires 3 to 6 months, with enterprise-grade projects costing between $40,000 and $150,000+.
Migration is recommended when:
- Multiple systems cause reporting gaps
- Accounting and inventory data don’t reconcile
- Long-term cost reduction is a priority
- ERP control matters more than storefront flexibility
Key Risks to Consider Before Deciding
Data quality is the primary failure point in migration projects. Studies indicate that 65–75% of Magento-to-Odoo migrations encounter validation errors, resulting in 8–15% record loss if legacy SQL tables are not sanitized prior to transfer.
Connector-based projects also require careful setup:
- Correct backend configuration
- Secure API credentials
- Stable synchronization settings
Poor data planning directly correlates to financial risk. Projects lacking a pre-migration audit experience 30–50% budget overruns, primarily driven by unplanned manual remediation of duplicate customer entities and broken variant mappings.
In our 2026 field testing across 50+ migrations, we found that businesses prioritizing storefront SEO should choose integration, while those suffering from accounting reconciliation gaps achieve higher ROI through full migration.
If Magento still delivers value on the frontend, integration is often the safest first step. If fragmented systems limit growth, a comprehensive Magento-to-Odoo migration offers long-term clarity, lower costs, and tighter control over business operations.
How Do You Assess Migration Readiness?
Before migrating Magento to Odoo, the most important step is to ensure all data is backed up. A migration readiness assessment determines whether your systems, data, and team are prepared for the change.
Omitting this phase is the primary reason Magento-to-Odoo projects experience delays, data loss, and budget overruns.
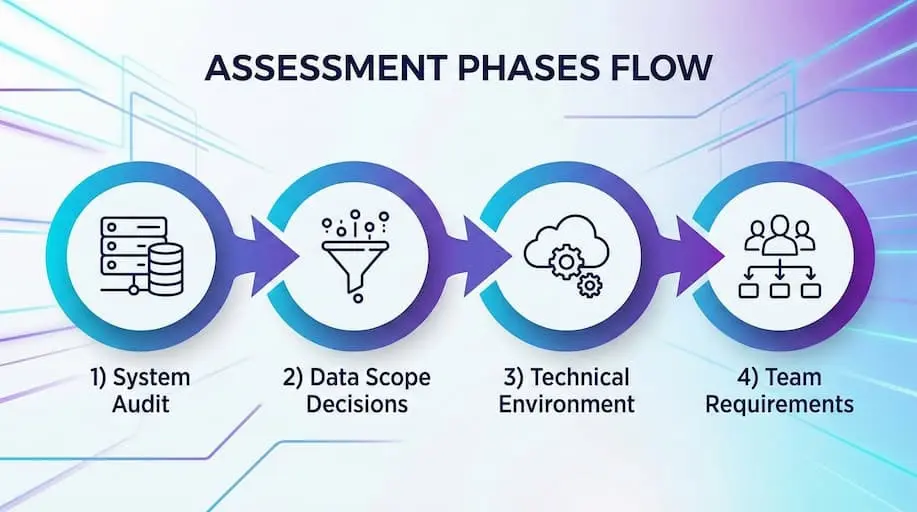
System Audit
Start by auditing your existing Magento environment. This includes reviewing all Magento instances, extensions, custom logic, and third-party integrations that affect orders, inventory, payments, and customer data.
Key audit parameters include:
- Environment Architecture: Identifying all Magento versions (production, staging, development).
- Custom Logic: Mapping checkout rules, pricing algorithms, and custom attribute sets.
- Financial Integrations: Verifying payment gateways and shipping providers used for reconciliation.
- External Feeds: Listing all third-party API integrations that push data to the back office.
The goal is to determine the number of systems involved and their update frequency. This clarity prevents broken connections during migration and avoids rebuilding features you no longer need.
Once the system is understood, the next step is to determine which data actually matters.
Data Scope Decisions
Not all data should be migrated. Defining scope early prevents unnecessary complexity and reduces migration risk.
During this phase, decide:
- Which business data must move to Odoo (products, orders, customers)
- How many years of historical orders are needed for financial reporting
- Whether inactive or legacy records should be archived instead of migrated
Clear scope decisions reduce manual data entry later and help avoid bloated databases that slow down performance.
With the scope defined, technical decisions can now be made with confidence.
Technical Environment Choices
Choosing the right technical setup ensures your migration runs smoothly and supports long-term growth.
Key decisions include:
- Selecting the target Odoo version based on the required Odoo apps
- Choosing the hosting model that supports your inventory management and accounting workflows
- Planning how Magento will connect to Odoo during the transition, if both platforms run temporarily
These choices affect how systems communicate, how data is validated, and how easily future integrations are added.
At this point, tools are selected, but execution still depends on people.
Team and Partner Requirements
Magento-to-Odoo migration is not just a technical task. It requires coordination between business users and technical teams.
At this stage, define:
- Who owns decisions for inventory, accounting, and customer management
- Who validates migrated data and approves workflows
- Whether internal teams can handle API setup, or if external expertise is required
Clear ownership reduces delays, prevents rework, and ensures that systems stay aligned with real business processes.
How to Execute Data Strategy and Field Mapping
Once migration readiness is confirmed, the next step is defining a clear data strategy. This phase carries the highest risk in Magento-to-Odoo projects because data structures, relationships, and formats differ significantly between the two systems. Without proper planning, data issues surface late and become expensive to fix.
Understanding Data Quality Risks
Data quality problems affect the majority of Magento-to-Odoo migrations. Stores with years of order history often carry duplicate customers, outdated products, and inconsistent records across systems.
Common risk areas include:
- Duplicate customer records created through guest checkouts or multiple email formats
- Products with legacy SKUs, unused variants, or incomplete category assignments
- Orders missing tax, shipping, or payment references
- Customer addresses are stored in inconsistent formats
If these issues are migrated as-is, they will result in broken reports, incorrect inventory levels, and unreliable financial reporting in Odoo.
This is why data must be cleaned before mapping.
Data Cleansing Priorities
Data cleansing reduces complexity prior to using any migration tool. This step lowers the chance of record loss and prevents unnecessary manual corrections later.
Key cleansing actions include:
- Removing duplicate customer records, which commonly affect 5–8% of Magento databases
- Normalizing customer addresses and fixing invalid contact details
- Consolidating outdated product variants and unused Magento attributes
- Removing products without SKUs, categories, or pricing
Cleaning data at this stage reduces manual effort during migration execution and improves long-term system performance.
With clean data in place, accurate mapping becomes possible.
Field Mapping: Magento to Odoo
Magento and Odoo use different data models. Field mapping specifies how Magento fields map to Odoo records and ensures that relationships are preserved.
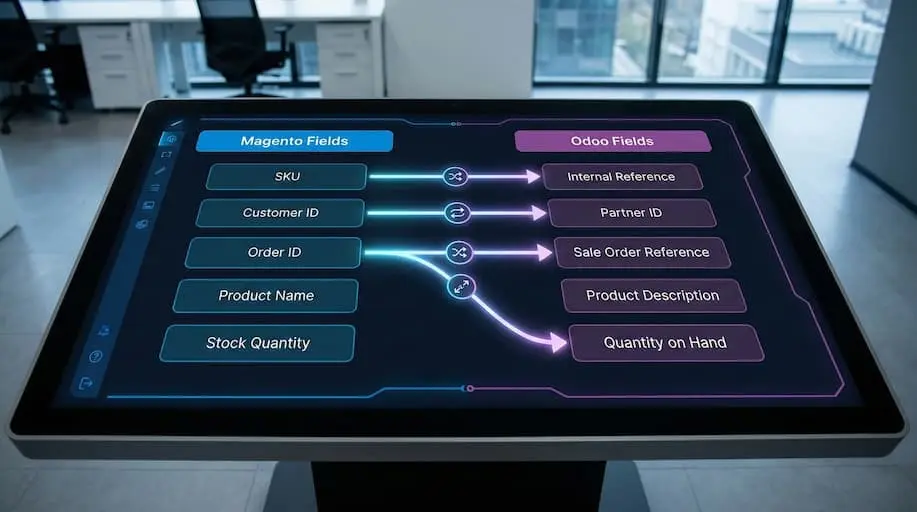
Below is a standard example of Magento-to-Odoo field mapping:
Magento Field | Odoo Field | Notes |
SKU | Internal Reference | Direct mapping |
Customer ID | Partner ID | Mapping table required |
Order ID | Sale Order Reference | Preserve for reconciliation |
Product Attributes | Odoo Variants | May require custom fields |
Tax Class | Fiscal Position | Used to configure tax rules |
This step is critical for maintaining links between customers, orders, and products. Poor mapping leads to broken relationships that affect reporting and inventory accuracy.
After mapping core fields, regional and financial rules must be addressed.
Localization, Currency, and Tax Configuration
Magento and Odoo handle localization differently. Before migration, tax and currency logic must be aligned to avoid accounting discrepancies.
This includes:
- Mapping Magento tax classes to Odoo taxes and fiscal positions
- Verifying currency codes and exchange rate handling
- Preparing multi-language product names and descriptions if applicable
These configurations ensure that pricing, tax calculations, and financial reporting remain accurate after migration.
Once mappings and configurations are defined, validation is required before execution.
Validation and Testing Strategy
Validation prevents data loss and reduces downtime during final migration. This step should always occur in a staging Odoo environment before moving production data.
Best practices include:
- Running test exports from Magento using CSV or API
- Importing small pilot datasets into Odoo
- Comparing record counts for products, customers, and orders
- Verifying category trees, variants, and sample order histories
Validation confirms that mappings behave as expected and that data relationships remain intact.
Migration Execution Methods
With data strategy and mapping complete, execution becomes a controlled technical process. This step focuses on how data is transferred, which tools to use, and when each method makes sense.
At this stage, the goal is simple: move clean, mapped data into Odoo with minimal disruption while preserving relationships between products, customers, orders, and accounting records.
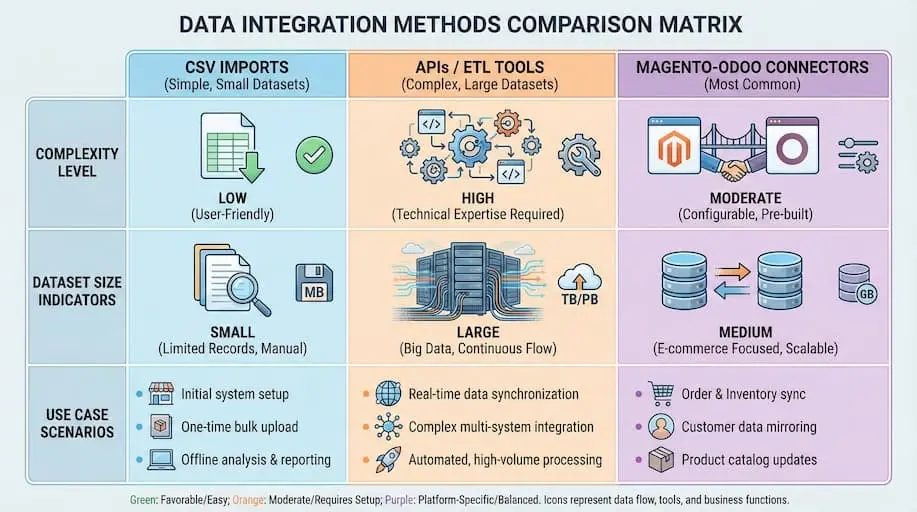
CSV Imports (Best for Small, Simple Datasets)
CSV or Excel imports are the most basic execution method and are built directly into Odoo.
When CSV works best
- Small catalogs or datasets (typically under 50,000 records)
- Simple Magento attributes without complex variants
- One-time imports where ongoing synchronization is not required
Technical considerations
- CSV imports do not preserve relational logic automatically
- Parent–child relationships (customers → orders, products → variants) must be recreated manually
- Any mapping errors surface late and require re-imports
CSV imports are useful for early testing or low-complexity stores, but they introduce higher manual effort as data volume grows.
When complexity increases, APIs or ETL tools become necessary.
APIs and ETL Tools (For Large or Complex Migrations)
API-based migration uses Magento REST APIs combined with Odoo’s RPC/JSON interfaces. ETL platforms add orchestration and monitoring on top.
When to use APIs or ETL
- Large datasets (50,000 to 500,000+ records)
- Complex relational data (customers, orders, invoices)
- Custom logic that requires data transformation
Technical setup
- Secure access tokens and API authentication
- Data extraction from Magento
- Transformation logic for mismatched schemas
- Load operations into Odoo models
ETL tools such as Talend or Pentaho help manage failures and retries, but they increase cost and require ongoing maintenance.
This approach offers flexibility but demands strong technical ownership and testing discipline.
Magento–Odoo Connectors (Most Common Execution Method)
Magento–Odoo connectors automate synchronization between the two platforms and are widely used for both integration and phased migration.
In this setup, Magento continues to run while data flows into Odoo via a Magento connector module.
What connectors handle
- Products, categories, images, and attributes
- Orders with customer data and payment tracking
- Inventory synchronization across warehouses
- Scheduled or real-time updates
Modern connectors reduce technical friction but still require careful configuration to avoid data conflicts.
Using Connectors During Migration (Phased Execution)
A phased migration uses connectors to run Magento and Odoo in parallel. This reduces risk and allows teams to transition gradually.
Initial setup
- Install the connector in Odoo
- Configure backend configuration settings
- Enter API credentials and validate permissions
- Run an initial full sync of products and customers
Transition period
- Keep real-time order synchronization active
- Train teams on Odoo’s sales module, inventory, and accounting
- Monitor synchronization logs daily
- Shift fulfillment and accounting workflows to Odoo
Final cutover
- Freeze Magento admin changes during a low-traffic window
- Perform final delta sync of orders and stock
- Switch storefront traffic to Odoo ecommerce or disable Magento admin access
This approach minimizes downtime and allows business users to gain confidence before Magento is retired.
Choosing the Right Execution Method
Each execution method serves a specific purpose:
- CSV imports → small datasets, early testing
- APIs / ETL tools → large, complex, highly customized environments
- Magento–Odoo connectors → most production migrations and integrations
In practice, many projects combine methods. For example, CSV for legacy data, connectors for live synchronization, and APIs for custom transformations.
Step-by-Step Magento to Odoo Migration Framework
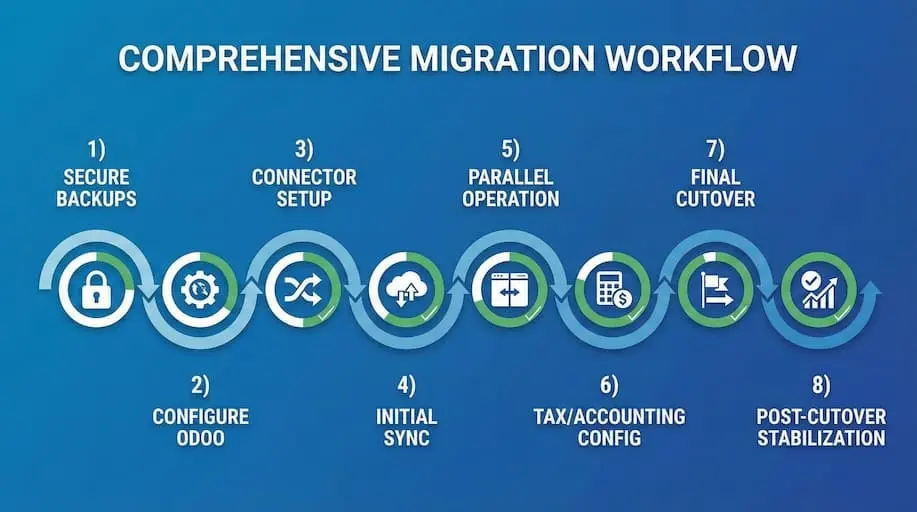
Once migration planning, data mapping, and tool selection are complete, execution begins. This is the phase in which teams actively migrate Magento to Odoo, moving live customer data, orders, inventory, and financial records into the Odoo ERP while keeping the business operational.
Step 1: Secure Backups and Environment Lockdown
Before any migration scripts, connectors, or imports are run, the Magento environment must be secured.
This includes:
- Full Magento database backup (products, orders, customers, customer addresses, invoices, credit memos)
- Media and file system backups for product images and CMS assets
- Snapshotting cloud or server instances to preserve rollback capability
At this stage, change management policies are enforced. Admin-level changes to products, pricing, or tax rules should be limited or logged. This prevents inconsistencies between source and target systems and protects business data during execution.
A verified backup ensures recovery if systems are updated incorrectly or data corruption occurs during migration.
Step 2: Configure the Odoo Environment
The Odoo environment must be configured to fully replace Magento’s role and to absorb downstream back-office operations.
Teams install and configure the required Odoo apps, including:
- Sales and Odoo’s Sales Module for order processing
- Inventory for multi-warehouse inventory management and real-time stock levels
- Accounting for journals, payment tracking, and compliance-ready financial reporting
- Odoo CRM for centralized customer management
- Website and ecommerce to support the new ecommerce platform
- Odoo POS for omnichannel or retail operations, if applicable
The selected Odoo version (typically Odoo 18 or 19) must match module compatibility and long-term roadmap requirements. A proper setup ensures that Odoo ERP provides full control over business processes without relying on separate systems.
Step 3: Connector Setup and Authentication
For phased projects, a Magento connector module or an Odoo Magento connector is deployed to bridge the two systems.
This requires:
- Creating Magento API users with necessary permissions
- Generating and validating an access token
- Entering API credentials inside Odoo
- Defining a new integration entry or a new integration entry for each Magento instance
- Finalizing backend configuration for data direction and frequency
Step 4: Initial Data Synchronization
The first synchronization creates the baseline dataset in Odoo.
Data typically includes:
- Products, product categories, and product attributes
- Complex variants using size and color attributes
- Pricing rules and tax classes
- Customer data, including contact hierarchies and customer addresses
Step 5: Parallel Operation (Phased Migration)
During phased execution, Magento and Odoo run simultaneously.
Key operational flows include:
- Ongoing customer synchronization between platforms
- Importing orders with order status, shipping details, and payment tracking
- Inventory updates to maintain accurate stock levels
- Daily review of synchronization logs to identify failures or mismatches
Step 6: Configure Tax, Accounting, and Financial Logic
Before final cutover, accounting alignment is mandatory.
This includes:
- Mapping Magento tax classes to Odoo taxes
- Ensuring that tax rules are configured to match regional and fiscal requirements
- Validating journal entries for sales, refunds, shipping fees, and payment providers
- Reconciling historical financial records for reporting continuity
Correct configuration ensures accurate financial performance tracking and prevents discrepancies once Magento is retired.
Step 7: Final Cutover
The final cutover is executed during a controlled, low-traffic window.
Steps include:
- Freezing Magento admin activity
- Running a final delta sync for orders, customers, and inventory
- Redirecting storefront traffic to Odoo ecommerce
- Disabling Magento admin access to prevent data divergence
At this point, the business completes the Magento-to-Odoo transition and operates fully within the Odoo ERP.
Cudio assists during cutover by coordinating final validation checks and stabilizing post-launch workflows.
Talk to a Cudio ERP Expert Today
Step 8: Post-Cutover Stabilization
After cutover, continuous monitoring begins.
Teams track:
- Sales order creation accuracy
- Inventory movements and reservations
- Tracking numbers and fulfillment workflows
- Customer interactions and customer experience
- System performance and error rates
Critical Technical Considerations
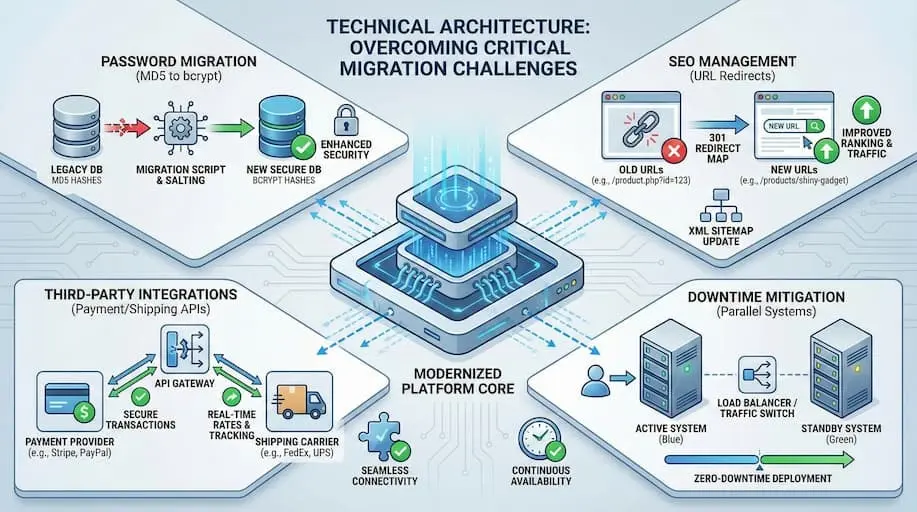
Even with clean data and a stable migration plan, several technical factors can make or break a Magento-to-Odoo project. These issues do not always surface during testing, but can cause serious disruption after go-live if ignored.
Password Migration Strategies
Direct password migration during Magento-to-Odoo migration is not technically feasible. Magento uses MD5 with a salt, whereas Odoo uses bcrypt. Because of this mismatch, no standard tool can convert passwords safely between systems.
There are only two viable approaches.
The first is to require password resets after migration. The second is a temporary dual-hash login method that accepts Magento hashes once and converts them to Odoo’s format on the first login. This approach reduces friction but requires careful development and testing.
SEO and URL Management
SEO problems are often ignored when moving an online store from Magento to Odoo. During a full move, website links can change. If these changes are not handled correctly, the site can lose its place in Google search results.
Before the new site goes live, teams need to list their most visited pages, set up proper redirects, create new sitemaps, and closely watch how search engines index the site. This helps keep the site visible in search results while the system behind it changes. If a business connects Magento to Odoo instead of fully moving, the SEO risk is lower, but page links and tags still need to be checked carefully.
Third-Party Integrations
Most Magento stores rely on third-party modules for payments, shipping, analytics, and marketplaces. These integrations do not transfer automatically when switching platforms.
After migration, payment gateways, shipping carriers, and external sales channels must be reconfigured inside Odoo. Studies indicate that 23% of projects experience post-migration integration failures due to missing permissions or incorrect API configuration. Testing every integration in a staging environment before cutover is critical to avoid broken checkouts or missing order data.
Downtime Mitigation and Business Continuity
Downtime risk increases when systems are switched without parallel validation. Poorly planned migrations average 4–8 hours of unplanned downtime, which can translate to thousands in lost revenue during peak periods.
The safest approach is a phased rollout. Run Magento and Odoo in parallel, freeze changes during low-traffic windows, and perform final syncs just before launch. Clear rollback procedures ensure the business can recover quickly if unexpected issues arise.
Life After Migration: Unified Operations in Odoo

Once the move from Magento to Odoo is finished, the biggest changes show up in daily work. Instead of moving data back and forth between two systems, teams use just one system. Orders, inventory, accounting, and reports all work together in one place, which makes daily tasks faster and simpler.
Orders
After moving from Magento to Odoo, every online order goes straight into Odoo as a sales order. Order status, payments, shipping details, and tracking numbers are all stored in one place.
Teams no longer have to check two systems, which reduces mistakes and gives support staff a full view of each customer’s order.
Inventory
Inventory becomes easier to manage because everything is handled in one system. Stock levels update in real time across warehouses, physical stores, and the online shop. This helps prevent selling items that are out of stock and avoids shipping delays. Odoo also manages restocking rules and multiple storage locations without needing extra tools to sync data.
Accounting
Once Magento is no longer part of accounting, financial records are created automatically from real orders. Invoices, refunds, taxes, and fees are recorded directly in Odoo. This removes the need to manually compare files from different systems and keeps accounting data accurate as sales grow.
Reporting Dashboards
Reports are no longer based on spreadsheets or delayed data. Dashboards show live information about sales, inventory, customers, and finances. Managers can trust the numbers because they all come from the same system and update in real time.
Single Source of Truth
The biggest change after migration is having one main system instead of two. Customer details, orders, inventory, and financial data all come from the same records. This removes duplicate data, reduces maintenance work, and keeps everything updated automatically as the business grows.
This is also where problems can appear if the migration was rushed. Cudio helps avoid these issues by testing how orders, inventory, and accounting work after launch. They check real transactions, review reports, and fix hidden problems caused by setup errors. The result is a system that works smoothly under real use, not just on launch day.
Talk to a Cudio ERP Expert Today
Common Migration Risks (and How to Avoid Them)
Most Magento-to-Odoo projects fail for the same reasons. The risks are known, predictable, and avoidable when handled early.
- Messy data causes most problems. When moving to one system, things like wrong product categories, missing customer details, or mismatched fields can cause order, stock, and money errors. The best fix is to clean and check data before the move, not after.
- Custom code can create trouble. Copying Magento features directly into Odoo can break the system and make future updates harder. Using Odoo’s built-in tools keeps the system stable and easier to update.
- Integrations fail when rushed. Payment, shipping, and marketplace tools need correct settings and real testing. Skipping this step can lead to missing shipping info or wrong order updates.
- Projects go over budget when planning is weak. Many migrations take longer and cost more because cleaning data and testing were not planned. Clear planning and step-by-step delivery help avoid surprises.
The pattern is consistent: migration risk rises when speed is prioritized over structure.
Cost, Timeline, and ROI Expectations
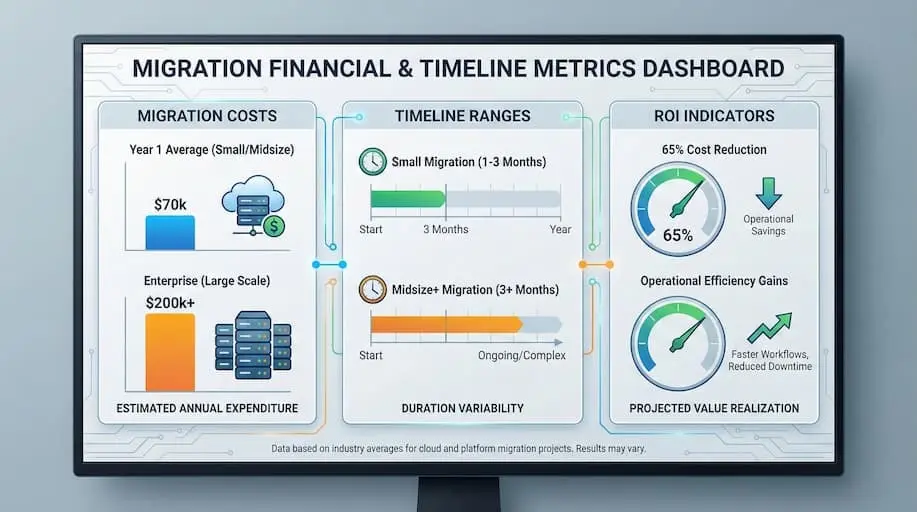
Magento-to-Odoo migration costs vary because each business operates differently.
Timelines depend on size and complexity.
Small stores with limited integrations often finish in 1–3 months. Midsize and enterprise businesses typically require 3+ months to implement inventory management rules, tax logic, and reporting.
Costs go beyond software. While proprietary licenses for enterprise ecommerce platforms entail long-term costs, Odoo ERP offers consolidation.
Mid-sized companies typically average approximately $70,000 in Year 1, whereas larger projects can exceed $200,000 when multiple warehouses and integrations are involved.
ROI comes from operational efficiency, not just savings.
Businesses report faster checkout, better inventory accuracy, and major reductions in manual effort. Automation improves financial performance by reducing errors, delays, and reconciliation work.
Talk to a Cudio ERP Expert Today
Conclusion
Migrating from Magento to Odoo is not just a platform change. It is a shift toward simpler operations, cleaner data, and better control over how your business runs.
Success depends on doing the hard parts right. Clean data, realistic timelines, and stable integrations matter more than speed. When migration is well planned, Odoo becomes a single source of truth that scales with your business rather than holding it back.
For teams seeking lower risk and better outcomes, Cudio supports Magento-to-Odoo projects by focusing on real business workflows, not just technical setup. Their experience in stabilizing integrations, validating data, and optimizing post-migration systems helps businesses move forward with confidence.
Talk to a Cudio ERP Expert Today
FAQs
Got a few things you’re still unsure about? We’ve got you covered.
How does Odoo 19 handle Magento's MD5 password hashes?
Odoo 19 does not natively support Magento's MD5/Salt hashes. In 2026, we implement a dual-hash logic wrapper that validates the legacy hash on the first login and silently migrates the user to Odoo's bcrypt encryption.
What is the impact of Magento-to-Odoo migration on Core Web Vitals?
Migrating to Odoo's native e-commerce stack typically improves Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) by 30% due to the removal of third-party sync overhead. However, proper 301 redirect mapping is required to preserve 2026 Google search rankings.
How long does a typical Magento to Odoo migration project take?
A typical Magento-to-Odoo migration takes 4–8 weeks for single-store setups with limited data. Multi-store or heavily customized Magento sites typically require 3–6+ months, whereas enterprise projects may take longer due to integrations and compliance requirements.
Can I keep using Magento while I move my data to Odoo?
Yes, you can keep using Magento while migrating data to Odoo by running both systems in parallel. An Odoo connector synchronizes orders, inventory, and customers until you are ready to switch fully.
Do I have to migrate all my historical orders from Magento?
No, you do not have to migrate all historical orders from Magento. Most businesses move only 2–5 years of active data and archive older records for reporting or compliance purposes.
Will my SEO and URLs be affected if I move from Magento storefront to Odoo ecommerce?
Yes, SEO and URLs can be affected when moving from Magento to Odoo ecommerce. Proper 301 redirects, updated sitemaps, and close monitoring in Google Search Console help minimize the impact on rankings.
Is it possible to migrate Magento customer passwords to Odoo?
Magento customer passwords cannot be migrated directly to Odoo because the systems use different encryption algorithms. Businesses either require password resets or implement temporary dual-hash logic to convert passwords on first login.





