ERP Implementation Checklist: Step-by-Step Guide for Success in 2026
Last Updated: October 14, 2025



Need a reliable ERP implementation checklist? This guide provides you with clear steps to ensure your ERP rollout is smooth and successful. From setting objectives to post-implementation support, follow this checklist to cover all critical aspects and avoid common pitfalls.
Phase 1: Planning the Route

Every successful ERP implementation project begins with solid planning. This phase sets the tone for the entire implementation process, establishing the vision, scope, and measurable goals that define project success.
Define Business Objectives
Start by defining the business objectives that the ERP system will support. Your goals should align directly with your company’s broader business strategy.
Whether it’s improving financial reporting, streamlining inventory management, or enhancing customer relationship management, your ERP implementation checklist should tie each objective to measurable outcomes.
Checklist for Business Objectives:
- Identify top-level business goals for ERP implementation
- Define measurable KPIs, such as reduced order processing time or improved reporting accuracy
- Align ERP objectives with departmental targets
- Define the MVP (Minimum Viable Product) for Phase 1 by focusing on your most urgent and high-impact pain points
- Keep Phase 1 simple and targeted. Many organizations see significant benefits in addressing just a few critical issues early in the process.
- Do not simply migrate existing processes to a new system; instead, carefully evaluate and optimize them. Use this opportunity to review how things are done today and define what the ideal process should look like in the latest ERP.
- Ensure that goals reflect both immediate wins and long-term digital transformation objectives.
Assemble the ERP Project Team
The ERP project team is the driving force behind a successful implementation. It should include a project manager, technical specialists, end-users, and representatives from key business units. These key business units include finance, supply chain, and human resources.
Checklist for Building the ERP Project Team:
- Appoint an experienced project manager to oversee all phases.
- Include department heads to represent key stakeholders.
- Define clear roles and responsibilities.
- Schedule weekly status meetings to ensure progress.
Conduct a Comprehensive Business Analysis
Understanding current business processes is crucial. Evaluate workflows, data management, and system dependencies. Be sure to document inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement.
Once a vendor and implementation partner like Cudio is selected, these processes should be revisited in more detail. This stage involves defining use cases to represent how your ideal future processes should function. Cudio brings proven best practices and deep industry knowledge to help shape these use cases for maximum impact.
Checklist for Business Process Analysis:
- Document current workflows across departments
- Identify manual tasks that can be automated
- Highlight pain points in data accuracy, reporting, or multiple systems
- Evaluate compliance with industry-specific regulations
- Revisit these processes with your ERP implementation partner to define use cases that reflect ideal future operations
ERP Planning and Vendor Evaluation
Selecting the right ERP system is one of the most critical decisions in the ERP implementation process. Evaluate ERP vendors for reliability, scalability, and support services. Review both on-premise and cloud ERP options to determine which best aligns with your operational model.
Vendor Evaluation Checklist:
- Compare ERP software capabilities and module flexibility.
- Evaluate the ERP vendor’s experience in your industry.
- Assess customer reviews and support responsiveness.
- Assess customer reviews, case studies, and the responsiveness of long-term support.
- Request demos of potential ERP solutions before final selection.
- Verify whether the vendor offers comprehensive implementation services or collaborates with certified partners.
- Evaluate potential implementation partners for their technical expertise, migration process, and ability to support your business complexity.
Develop the Project Charter and Timeline
Your project charter defines objectives, timelines, resources, and scope. It ensures that all key stakeholders share a unified understanding of the ERP implementation project.
However, the project charter and timeline should only be finalized after selecting your ERP vendor and implementation partner. These partners play a critical role in shaping the project scope, identifying potential risks, and ensuring the timeline is realistic based on your chosen platform and level of complexity.
Checklist for Project Planning:
- Create a realistic project timeline with defined milestones.
- Identify dependencies between tasks and deliverables.
- Define resource allocation and budget distribution, including dedicated time for super users to participate fully in the implementation.
- Secure leadership approval for the final plan and ensure department leads are empowered to make decisions during the project.
This phase establishes the solid foundation required to support the entire implementation journey. Although this process may seem challenging, Cudio is here to guide you every step of the way. We specialize in seamless Odoo migration services to help businesses upgrade from outdated systems with confidence.
Learn More About Our Odoo Implementation Services
Phase 2: Designing the System
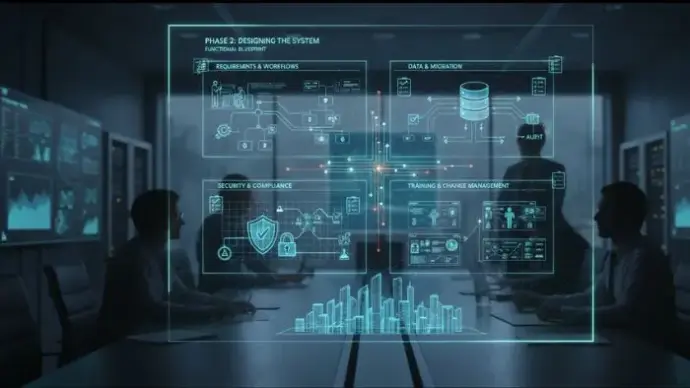
The design phase translates planning into a functional blueprint for your new ERP system. It focuses on process mapping, data structure, and customization requirements that define how your ERP platform will operate.
Gather and Document ERP Requirements
Gathering input from all user groups ensures that your ERP system reflects real operational needs. Each department should identify functional and technical requirements that contribute to overall efficiency.
Checklist for ERP Requirements Gathering:
- Conduct workshops with department heads and end users.
- Document functional requirements for each process.
- Identify non-functional needs such as scalability and performance.
- Prioritize critical requirements that directly affect business outcomes.
Map Business Processes and Workflows
Create detailed visual maps to illustrate how existing business processes will adapt to the ERP system. Identify redundant steps and bottlenecks that can be eliminated.
Checklist for Process Mapping:
- Chart current workflows across all departments.
- Align ERP system functions with business processes.
- Identify opportunities to streamline operations.
- Validate process maps with key stakeholders.
Define Data Architecture and Migration Plans
Data migration is one of the most challenging aspects of any ERP software implementation. Correctly mapping and cleaning existing data ensures accuracy during transfer.
Checklist for Data Migration Planning:
- Audit existing data for accuracy and completeness.
- Establish data ownership and accountability.
- Create a metadata import template for consistent formatting.
- Conduct pilot tests to verify the data transfer process.
Incorporate Security and Compliance Measures
Designing for data protection and compliance ensures your ERP implementation meets industry standards. Consider how sensitive financial records and human resources data will be stored and accessed.
Security Checklist:
- Implement role-based access controls.
- Include encryption for sensitive data.
- Review compliance with industry-specific regulations.
- Schedule regular security audits.
Plan for User Training and Change Management
Preparing employees for a new system requires structured user training and a clear change management plan.
Checklist for Training and Change Management:
- Develop training plans tailored to each department.
- Conduct hands-on training sessions for end users.
- Create communication plans to manage expectations.
- Identify change champions to encourage adoption.
Designing with scalability and usability in mind builds a system that supports long-term growth and digital transformation.
Phase 3: Building and Configuring the ERP System
In this phase, the ERP project team brings the blueprint to life. System configuration, customization, and testing ensure that the ERP platform meets defined ERP requirements and business goals.
Configure Core Modules and Integrations
Configure ERP modules, including finance, supply chain, inventory management, and customer relationship management. Integrate the ERP system with external platforms to unify operations and streamline processes.
Checklist for System Configuration:
- Set up modules according to design specifications.
- Integrate ERP software with third-party applications.
- Verify functionality through initial test runs.
- Review module dependencies and workflow alignment.
Data Migration Execution
Migrating data requires precision and validation. Follow your predefined migration plan to ensure successful import without data loss.
Checklist for Data Migration Execution:
- Back up all historical data from legacy systems.
- Conduct test migrations to verify data accuracy and integrity.
- Validate imported data through reconciliation reports.
- Review data integrity with accounting and human resources teams.
Custom Development and System Testing
Customizations enhance the ERP software’s flexibility and align it with specific business needs. Conduct multiple rounds of testing to ensure stability and performance.
Checklist for Customization and Testing:
- Develop custom modules or reports as needed.
- Conduct unit, system, and user acceptance testing.
- Document results and resolve issues.
- Validate that integrations maintain consistent data accuracy.
Document Use Cases and Build Knowledge Resources
Before training begins, it is essential to document each use case developed during the design phase thoroughly. These use cases define how each process should work within the ERP system and serve as the foundation for consistent, practical training.
We recommend creating short video walkthroughs for each use case and storing them in Odoo’s built-in eLearning module. This creates a central knowledge hub that supports onboarding, training, and long-term process clarity across the organization.
Checklist for Use Case Documentation:
- Document each use case with clear steps, expected outcomes, and responsible roles.
- Record short instructional videos showing how each process is executed in the system.
- Upload and organize videos in Odoo’s eLearning module.
- Keep documentation up to date as changes or improvements are made.
Train the ERP Project Team and End Users
Training ensures confidence in using the new ERP system. The ERP project team should conduct ongoing sessions that combine technical training with process understanding.
Training Checklist:
- Provide hands-on training for end users.
- Update training materials as changes are made.
- Offer refresher courses before go-live.
- Encourage collaboration through user groups.
This phase is the bridge between planning and real-world execution, turning ideas into actionable systems that enhance productivity.
Phase 4: Deployment

Deployment is where all preparation and testing come together. Working with a Cudio as your implementation partner ensures a well-planned go-live strategy and that the project launches smoothly.
Conduct Final Data Validation
Before the go-live date, perform comprehensive checks to confirm data accuracy and integrity. Verify that all data migration and system configurations are complete.
Checklist for Data Validation:
- Compare pre- and post-migration reports for consistency.
- Review financial reporting outputs.
- Test real-world transactions for accuracy.
- Obtain approval from the project manager and key stakeholders.
Prepare for Go-Live
Effective go-live preparation minimizes disruption across the entire organization. Communicate clearly with users about the transition plan and contingency measures.
Checklist for Go-Live Preparation:
- Announce the go-live schedule organization-wide.
- Test all system integrations and workflows.
- Establish a help desk for immediate user support.
- Conduct final user acceptance testing.
Monitor System Performance After Launch
Continuous monitoring during the first weeks post-launch helps identify and fix any performance issues quickly.
Checklist for Early Monitoring:
- Track ERP system response times.
- Record user feedback and reported issues.
- Review transaction logs for anomalies.
- Prioritize fixes based on business impact.
Encourage Adoption and Provide Support
Post-launch user support is key to achieving full adoption of the new system.
Checklist for Adoption Support:
- Conduct daily stand-ups for user feedback.
- Provide quick reference guides for common tasks.
- Reinforce training through mentorship programs.
- Celebrate milestones to encourage adoption.
A structured deployment ensures a smooth transition to your new ERP system with minimal downtime and disruption.
Learn More About Our Odoo Implementation Services
Phase 5: Post-Implementation Support and Continuous Improvement

Once your ERP system is live, the journey continues through continuous improvement, user support, and ongoing maintenance. This ensures that your ERP platform remains a valuable asset for years to come.
As part of our post-implementation services, Cudio provides clients with access to our Accounting and Database Health Dashboard. This tool continuously monitors the health of your ERP system, helping to identify data inconsistencies, performance issues, and configuration risks before they escalate into larger problems. It supports proactive maintenance and gives your team real-time visibility into critical system metrics.
Learn More About Our Odoo Implementation Services
Ongoing Maintenance and System Optimization
Regular updates and performance reviews keep your ERP implementation aligned with evolving business needs.
Checklist for Ongoing Maintenance:
- Schedule periodic updates and patches.
- Conduct quarterly system audits.
- Review integrations for performance consistency.
- Test backups and recovery plans.
Monitor KPIs and User Adoption
Evaluate how effectively your ERP system supports core business objectives. Use analytics to track KPIs such as user adoption rates, process efficiency, and reporting accuracy.
Checklist for KPI Tracking:
- Review dashboard analytics monthly.
- Gather user feedback across departments.
- Adjust workflows to increase efficiency.
- Update the training plan as new features are added.
Expand Capabilities and Drive Digital Transformation
As your organization grows, expand your ERP platform with additional modules to enhance performance in areas such as supply chain, manufacturing, and project management.
Checklist for Expansion and Optimization:
- Identify business areas that would benefit from automation.
- Evaluate potential ERP solutions for new functionalities.
- Plan phased implementation of new modules.
- Align expansion with business goals and strategies.
Empower Employees and Strengthen Culture
Empowering employees through continuous education ensures long-term success.
Checklist for Empowerment:
- Provide ongoing user training for new hires.
- Maintain a feedback system for improvement suggestions.
- Recognize teams that drive innovation through the ERP system.
Conclusion
ERP implementation is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing journey toward efficiency, transparency, and growth. With the right roadmap, ERP planning, and change management, your organization can navigate the complexities of enterprise resource planning confidently.
A comprehensive checklist transforms complexity into clarity, ensuring your ERP project team executes each phase with precision. From defining business objectives and managing data migration to providing user support and optimizing system performance, every step builds toward a successful implementation.
At Cudio, we specialize in guiding businesses through every phase of the ERP implementation process. Our experts provide valuable insights, proven frameworks, and dedicated support to ensure your ERP implementation delivers measurable value.
Your journey toward a successful ERP implementation starts today.
Learn More About Our Odoo Implementation Services
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is initial planning critical in ERP implementation?
Initial planning is essential in ERP implementation as it secures executive support, establishes a clear roadmap, and ensures sufficient resources are allocated. This foundational work significantly increases the likelihood of project success.
What common mistakes should be avoided when preparing an ERP BRD?
Avoid common mistakes when preparing an ERP Business Requirements Document (BRD) by ensuring strong stakeholder engagement, specifying clear and detailed requirements, considering scalability, setting realistic timelines and budgets, and balancing features with overall business goals. This approach will lead to a more effective ERP implementation.
What is the first phase of ERP implementation?
The first phase of ERP implementation is discovery and planning, focusing on assessing the organization's needs, challenges, objectives, and budget for a successful transition. This foundation is crucial for guiding the project effectively.
Why is stakeholder engagement important in the preparation of an ERP BRD?
Stakeholder engagement is essential in preparing an ERP BRD as it guarantees that all relevant business requirements are captured, reducing the risk of overlooking critical needs and ensuring a comprehensive solution. This collaborative approach ultimately leads to a more successful ERP implementation.
How can organizations ensure user training is effective post-deployment?
To ensure effective user training post-deployment, organizations should invest resources in ongoing technical support and regular updates while fostering user comfort with the system. This approach helps maintain proficiency and addresses any challenges users may face.


