An ERP implementation life cycle is a structured, multi-phase process used to guide the selection, design, testing, and deployment of an Enterprise Resource Planning system. This framework helps organizations manage complexity, mitigate risk, and align the new software with core business goals.
This guide explains the key phases of the life cycle, the different rollout strategies, and the critical factors for a successful implementation.
Key Takeaways
- An effective ERP implementation follows a structured life cycle consisting of discovery, design, development, testing, deployment, and support phases to ensure alignment with business needs.
- Choosing the right rollout strategy, big bang, phased, or hybrid, is crucial for minimizing disruptions and ensuring a smooth transition during ERP implementation.
- Critical success factors for ERP implementation include executive leadership support, comprehensive employee training, and utilizing external expertise to enhance project outcomes and user adoption.
What is an ERP System?
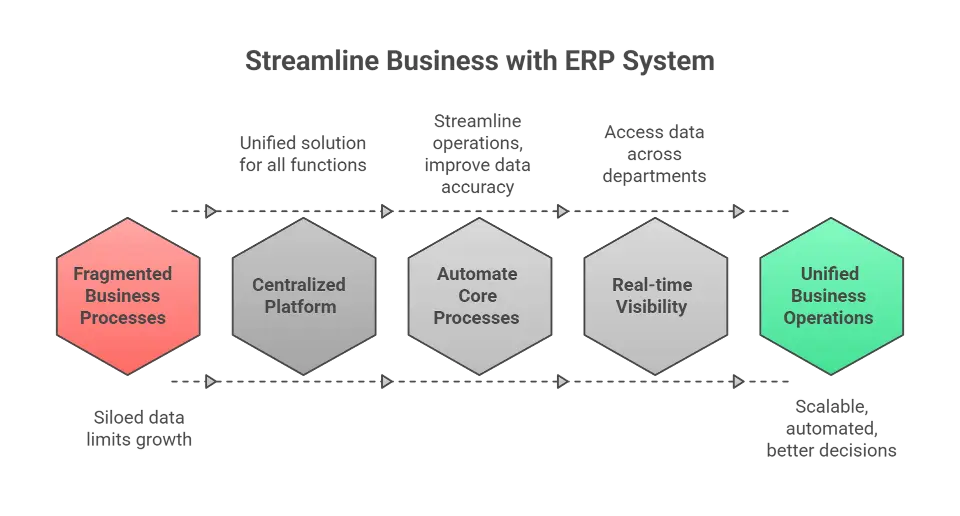
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a centralized software platform that brings together all your core business processes, from accounting and procurement to supply chain management and manufacturing. By managing these functions in a single system, ERP streamlines operations, improves data accuracy, and enables real-time visibility across departments.
With modern ERP systems, businesses can move away from spreadsheets and fragmented tools that limit growth. Instead, they gain a unified solution that supports scalability, automation, and better decision-making.
ERP software supports a wide range of departments:
- Accounting: Manage financial data, reporting, and compliance
- Procurement: Automate purchasing and vendor management
- Inventory & Supply Chain: Track stock levels, shipments, and demand forecasts
- Manufacturing: Optimize production schedules and quality control
If your business has outgrown spreadsheets, adopting the right ERP solution can unlock efficiencies and prepare you for future growth. Whether cloud-based or on-premise, today’s ERP systems offer powerful analytics, secure integrations, and configurable workflows to fit your exact business needs.
As we explore the ERP implementation life cycle, keep in mind how vital your ERP choice is. Collaborating with a reliable ERP implementation partner ensures the system fits your operations from the start and evolves with you over time.
Understanding the ERP Implementation Life Cycle
A successful ERP implementation isn’t just about installing software; it’s a step-by-step journey that touches nearly every part of your business. The ERP implementation life cycle outlines this journey, breaking it into key phases that help companies to plan, execute, and optimize their ERP systems.
This life cycle typically includes:
- Installing ERP software
- Migrating and cleaning data
- Setting up users and permissions
- Training employees to use the new system
Each of these tasks fits into a broader timeline that guides businesses from planning to long-term success. Understanding these phases helps ensure your ERP system continues to meet evolving needs, long after go-live.
A solid project management foundation is critical. It ensures your team doesn’t get bogged down by delays or overspending. The right ERP project team, backed by stakeholder input, helps anticipate challenges early and keeps the project on track.
For businesses that want expert guidance, a partner like Cudio can offer practical insights and implementation support. Whether you're navigating your first ERP deployment or improving an existing setup, our team brings proven frameworks and real-world experience to streamline the process.
What Are the Key Phases of the ERP Implementation Life Cycle
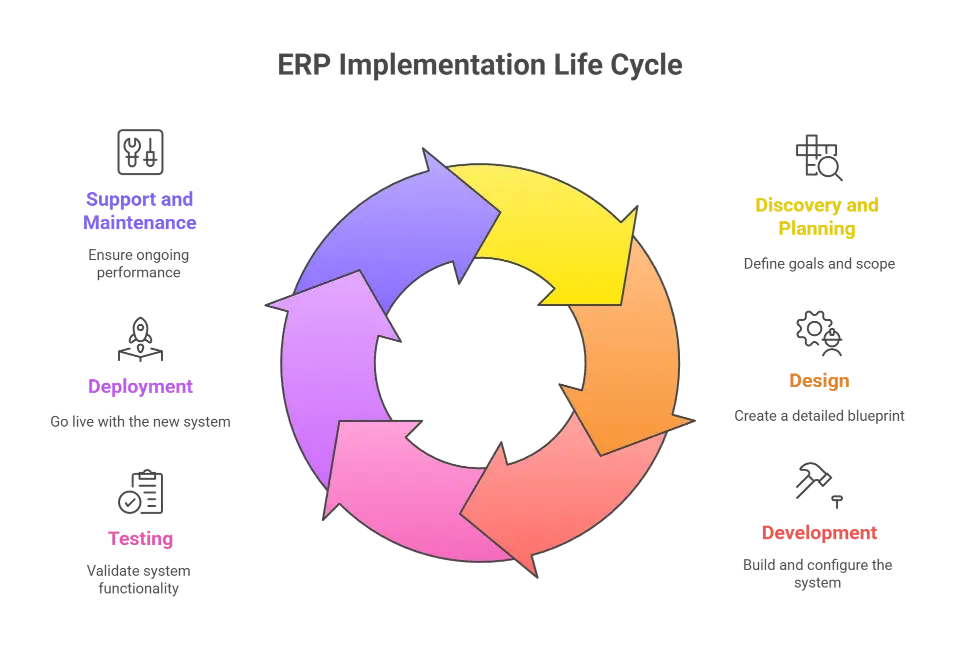
The key phases of the ERP implementation life cycle are Discovery and Planning, Design, Development, Testing, Deployment, and Support.
This structured approach provides a clear roadmap that guides the project from initial concept to long-term optimization. Each phase has specific goals and deliverables designed to build upon the last, ensuring all business requirements are met.
Following these distinct phases is the most effective way for organizations to mitigate risk, manage complexity, and avoid the common causes of ERP failure
The phases typically include:
- Discovery and Planning
- Design
- Development
- Testing
- Deployment
- Support
These stages remain consistent whether you choose a cloud ERP or an on-premise system, though specific steps may differ based on your existing IT infrastructure and organizational needs.
Discovery and Planning Phase
The Discovery and Planning phase is the foundational stage where the project's goals, scope, and roadmap are defined.
During this phase, the organization builds a project team, evaluates existing business processes, and performs a gap analysis to identify inefficiencies. This analysis is used to set measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and begin vetting vendors.
This initial planning is critical for aligning the ERP strategy with specific business goals and preventing the scope creep that derails many implementations.
Activities include:
- Building a dedicated project team, led by an experienced project manager, to oversee execution
- Evaluating existing business processes and identifying inefficiencies across departments
- Running a detailed gap analysis to uncover where current workflows fall short of business requirements
- Assessing existing IT infrastructure and legacy systems to determine upgrade needs
- Setting measurable key performance indicators (KPIs) tied to business outcomes like improved customer satisfaction, financial management accuracy, or inventory management control
At this stage, careful planning is critical to reducing scope creep and delays. It’s also when you should begin vetting potential vendors and identifying the right ERP solution that fits your operational model.
Early involvement from business users and top management ensures the entire organization is aligned with the ERP project’s objectives from the beginning.
Design Phase
Here, organizations translate insights from the planning phase into a detailed blueprint for the future ERP environment. The design phase is where alignment between software functionality and business strategy is fine-tuned.
Key steps include:
- Mapping existing processes and how they will adapt to the ERP platform
- Running workshops with functional teams to gather feedback
- Finalizing system configurations with minimal customizations for sustainability
- Co-developing new workflows using results from the gap analysis
- Designing for scalability and usability with long-term business growth in mind
A well-structured design blueprint ensures all software modules integrate correctly, which reduces costly development errors and delays in later phases. Avoiding unnecessary complexity at this point also reduces future upgrade risks.
Development Phase
This phase brings your blueprint to life. It includes system configuration, custom development, and migration preparation.
Key tasks include:
- Installing and configuring the ERP solution based on business requirements
- Migrating clean, validated existing data from multiple systems
- Establishing secure user roles and permissions
- Creating integrations with third-party apps or business-critical platforms
- Developing enhancements only where they support measurable ROI or user needs
Throughout development, industry best practices help ensure system performance meets expectations. Collaborating with an experienced implementation partner like Cudio at this stage can help streamline complexity and avoid delays.
Testing Phase
Testing validates that the system works as designed and aligns with real-world use cases. This phase reduces post-implementation issues and boosts end-user confidence.
Types of testing performed:
- Unit testing for individual features
- Integration testing across modules
- User acceptance testing (UAT) by business users to confirm functional fit
Real-world scenarios, such as processing a whole sales order or generating financial reports, are used to simulate live conditions. The project team documents, prioritizes, and resolves every issue found during testing to ensure the system performs effectively.
Testing also provides a final checkpoint to make any last-minute refinements to workflows, system configurations, or data integrity.
Deployment Phase
Deployment is the moment your new ERP system goes live. Choosing the right rollout strategy is essential. A big-bang approach may work for smaller businesses, while a phased rollout is better for larger, multi-departmental organizations.
Key steps include:
- Finalizing end-user training materials
- Hosting pre-launch walkthroughs with key teams
- Setting up support resources for real-time assistance
- Running parallel operations to ensure continuity
To avoid disruption, it's critical to plan for early adoption support. Clear change management communication helps set expectations across departments.
If you’ve partnered with Cudio, you’ll also benefit from expert go-live support, ensuring both your internal team and business users are fully prepared.
Support and Maintenance Phase
Post implementation, the focus shifts to continuous improvement. From our experience managing over 100 ERP rollouts, we have found this final stage is the most critical for long-term user adoption.
Our internal data shows that clients who maintain a formal support plan resolve 80% of user-reported issues within the first 30 days, which significantly improves trust in the new system.
Ongoing support involves:
- Monitoring system performance regularly
- Addressing support tickets and user feedback
- Running regular system audits to identify gaps or bottlenecks
- Updating training materials and onboarding new hires
- Planning for future scalability as the business evolves
End-user training doesn’t stop at go-live; it should evolve with system updates and business process changes. A post-implementation support plan, paired with analytics tied to key performance indicators, ensures your investment stays aligned with changing needs.
What Are the Different ERP Rollout Strategies?
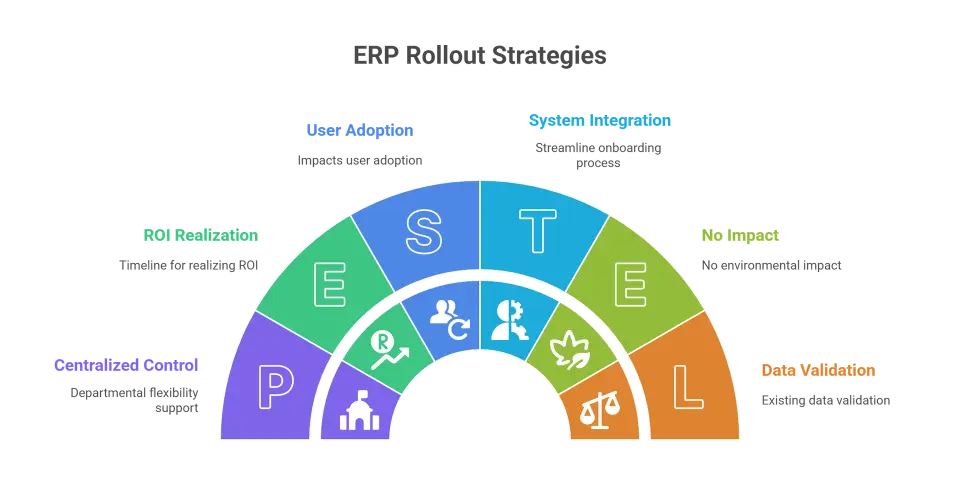
The three primary ERP rollout strategies are the Big Bang, the Phased Approach, and the Hybrid Approach.
A Big Bang rollout deploys all modules at once, offering a fast transition but carrying high risk. A Phased Approach implements the system module-by-module, which is slower but safer. The Hybrid model launches core functionalities first and rolls out secondary features later.
The choice of strategy is one of the most critical decisions in the life cycle, as it directly impacts user adoption, business disruption, and the timeline for realizing ROI.
Big Bang Approach
In the big bang rollout strategy, all ERP modules and locations go live at once. While this approach enables a fast transition and quicker return on investment, it also introduces a higher risk of disruption. A big bang rollout can work well for smaller organizations or those with simpler operational structures. However, fewer than 25% of organizations choose this route due to its operational risk.
Advantages:
- Rapid realization of benefits across departments like inventory management, financial management, and procurement
- Immediate access to a unified data environment and streamlined business management
Challenges:
- Increased risk of ERP failure if issues arise post-launch
- Requires extensive end-user training and system testing beforehand
If your organization is considering this path, it's crucial to evaluate whether your ERP solution is fully configured, tested, and ready to support all business users simultaneously. Learn more about how to avoid ERP implementation pitfalls.
Phased Approach
A phased rollout allows companies to implement ERP modules in stages across business units or geographic regions. This strategy supports a smoother transition by letting users adapt incrementally and minimizes the risk of major operational disruptions.
Benefits include:
- Ability to focus on specific business processes first, like warehouse management or sales
- Opportunities to gather feedback early and refine future rollouts
- Reduced risk from go-live errors, thanks to isolated deployments
Phased implementations work well for organizations with multiple systems or complex operations. They also help when legacy or existing data needs validation at each stage. If you're unsure which modules to prioritize, start with high-impact areas that align with your key performance indicators.
Hybrid Approach
The hybrid rollout strategy combines aspects of both big bang and phased deployments. It’s ideal for businesses that want to rapidly launch core functionalities—such as financials and reporting, while staging additional features over time.
For example, a business may roll out ERP financial modules in one phase, followed by CRM, manufacturing, or supply chain in later stages. This offers a practical balance between speed and risk management.
Why choose a hybrid?
- It supports both centralized control and departmental flexibility
- It accommodates the needs of the entire organization without overwhelming your ERP project team
For businesses using a cloud-based ERP like Odoo, the hybrid model can streamline onboarding while giving time for deeper integrations. Cudio has supported many organizations in tailoring this approach to their business growth goals and system capabilities.
How Long Does an ERP Implementation Take (And How Much Does It Cost)?
ERP implementation requires more than just installing software. It demands realistic expectations around time, budget, and resources. Understanding what drives project duration and cost helps organizations avoid unnecessary delays and financial overruns.
How Long Does an ERP Implementation Take?
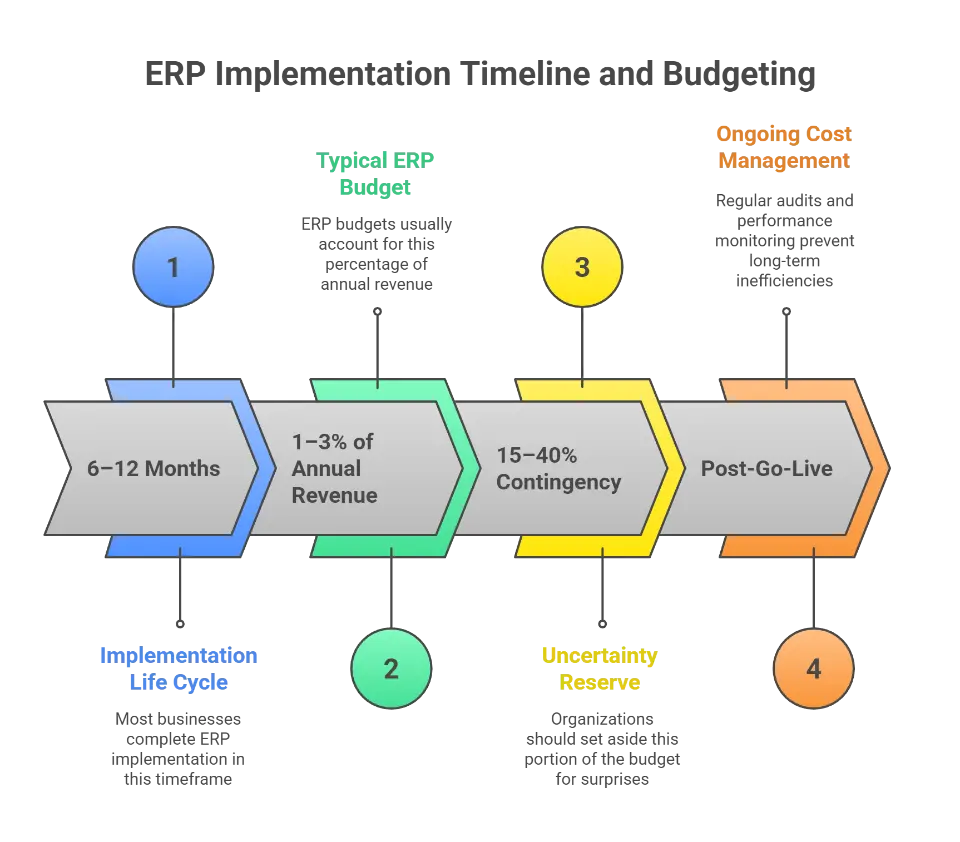
For most businesses, the ERP implementation life cycle spans 6 to 12 months. Timelines depend on the complexity of your operations, the customization required, and your existing IT infrastructure.
Mid-sized companies often complete implementation within a year, while larger enterprises may need more time due to multiple departments, legacy systems, or specialized workflows.
Organizations choosing cloud ERP platforms like Odoo may experience faster deployment timelines since many core modules are already optimized for rapid configuration.
How Much Should You Budget?
Costs vary widely based on the scope of the implementation:
- Large enterprises may invest between $500,000 and $2 million
- Mid-sized companies often spend between $150,000 and $750,000
- Typical ERP budgets account for 1 to 3 percent of annual revenue
Budgets should include licensing, implementation services, internal labor, and training. However, unexpected costs can emerge if the initial planning is incomplete.
Common cost escalators include:
- Data cleanup and restructuring of existing data
- Additional modules or marketplace integrations
- Post-implementation configuration or feature enhancements
- Delays due to unclear business requirements or scope changes
This detailed ERP budgeting guide covers how to avoid hidden costs and set clear expectations from the start.
Why Projects Go Over Time or Budget
ERP is a complex process that involves aligning technology with core business processes. Without careful planning, most ERP implementations risk delays or cost overruns.
Key factors that cause implementation timelines to slip:
- Insufficient internal staffing or expertise
- Over-reliance on customization
- Gaps in change management readiness
- Unanticipated licensing costs with cloud-based ERP platforms
Choosing a capable implementation partner and defining priorities early in the implementation phase can significantly reduce risks.
Planning for Uncertainty
To prepare for surprises, organizations should set aside 15 to 40 percent of the total ERP budget as a contingency reserve. This buffer helps cover unexpected tasks, such as adjusting to new compliance rules, revising data-mapping logic, or expanding user training.
Post-Go-Live Cost Management
After go-live, financial oversight should continue. Regular system audits and proactive performance monitoring prevent long-term inefficiencies.
Post-implementation considerations include:
- Tracking KPIs like system uptime and error rates
- Maintaining consistent system performance
- Addressing gaps in end-user training
- Reviewing cost-impacting requests for feature changes
Keeping your ERP aligned with business growth requires active oversight. As the system continues to evolve, so should your approach to optimizing its value and performance.
Why Are Cloud and SaaS ERPs Becoming More Popular?
More than 53% of organizations are adopting cloud-based ERP systems for cost savings and enhanced operational efficiency.
According to a 2024 market analysis from Forgestik, the cloud ERP market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 10.5%, potentially exceeding $70 billion by 2032.
The selection of cloud deployments increased year over year, with organizations citing scalability, modern analytics/AI capabilities, and integration advantages.
Industry-specific cloud ERP solutions are emerging to cater to the unique needs of sectors such as healthcare and manufacturing. The share of organizations choosing SaaS rose relative to prior years, reflecting priorities in cost control, accessibility, and faster time-to-value. This trend underscores the growing importance of cloud-based ERP systems in driving business growth and operational efficiency.
What Are the Critical Success Factors for an ERP Implementation?
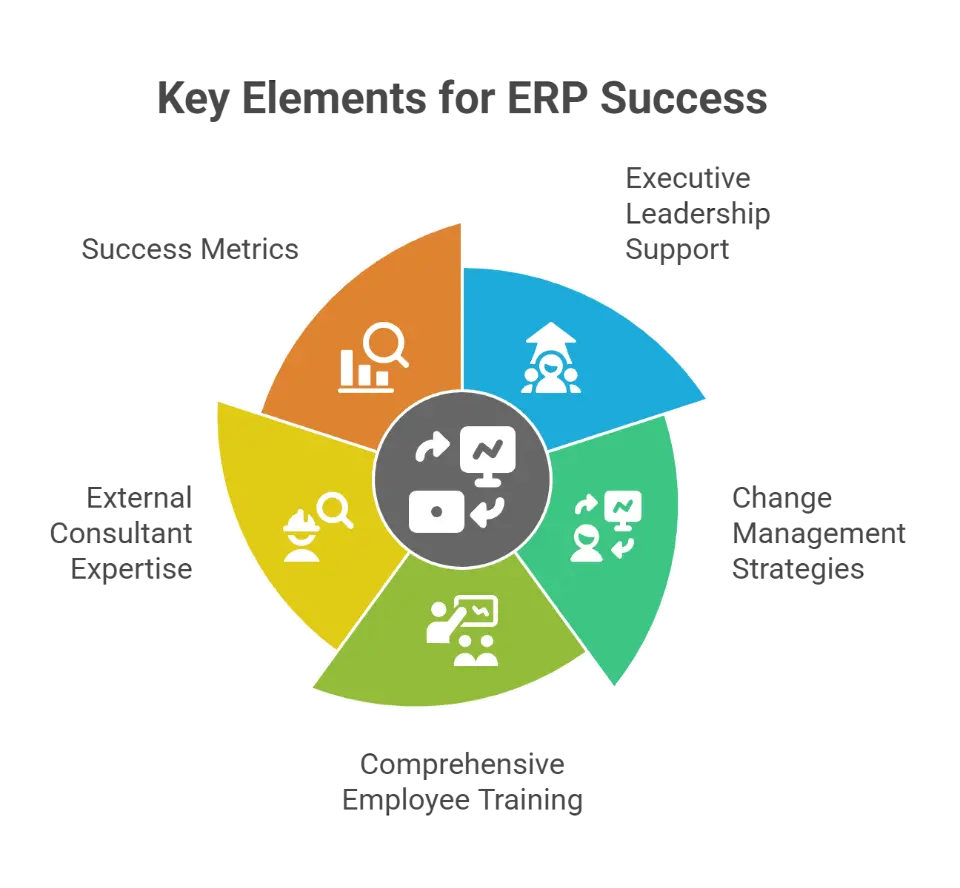
Executive leadership support is crucial for successful ERP implementation as it ensures projects receive the necessary resources and backing needed for organizational change. Having strong executive sponsorship unlocks resources and drives changes, ensuring the project stays on track. Effective change management strategies, such as clear communication and employee involvement in the process, can help alleviate resistance during ERP implementation.
Comprehensive employee training is essential; poor training can significantly diminish the effectiveness of the new ERP system. Investing in role-based end-user training and robust post-implementation support, aligned with industry best practices, is crucial to accelerate adoption and realize planned benefits.
Utilizing external consultants can enhance ERP implementation success by:
- Providing expertise and experience
- Ensuring on-time delivery
- Supporting benefits realization
- Stabilizing operations with trained users.
Success metrics for most ERP implementations include:
- On-time and on-budget delivery
- Benefits realization against quantified key performance indicators (KPI)
- Stabilized operations with trained users and sustained support cadence
These critical factors play a significant role in ensuring that the ERP system meets the organization’s business requirements and contributes to improved customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and customer relationship management.
What Are the Most Common ERP Implementation Pitfalls?
A significant challenge of ERP implementation is its time- and cost-intensive nature. Planning for potential pitfalls can benefit ERP implementation in the long run. Common issues include:
- The ERP system’s inability to integrate with other systems creates a need for new systems to compensate, which, in turn, increases the number of workarounds for staff.
- Failing to update an ERP leads to it becoming a legacy system, which causes a sharp increase in maintenance costs and support time.
- The ERP system is failing to meet business needs, resulting in operational inefficiencies.
The big bang strategy carries significant risks, including encountering major post-launch issues due to the lack of incremental testing. To avoid these pitfalls, organizations should plan for continuous improvement and agility, ensuring the ERP system evolves with the business needs. Practical change management and comprehensive training can also mitigate risks associated with user adoption and operational disruptions.
Understanding and planning for these common pitfalls helps organizations avoid ERP implementation delays and achieve a successful ERP implementation. Continuous monitoring and regular system audits are essential to ensure the ERP system continues to meet business requirements and supports growth objectives.
Final Words
Successfully managing the ERP implementation life cycle requires strategic planning, cross-functional alignment, and consistent execution. Each phase, from discovery to post-implementation support, plays a key role in ensuring the ERP system meets organizational needs and delivers lasting value.
With the right rollout strategy, thorough planning, and a committed project team, businesses can overcome challenges and minimize disruption. Cloud ERP adoption continues to rise, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency for companies aiming to stay competitive.
At Cudio, we specialize in helping businesses implement ERP systems that align with real goals and evolving needs. Whether you're planning your first ERP rollout or upgrading an existing system, our team is ready to support you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Find quick answers to common questions about ERP implementation, timelines, success factors, and best practices to help guide your project with clarity and confidence.
What is an ERP implementation life cycle?
An ERP implementation life cycle encompasses the stages involved in deploying ERP software, including discovery and planning, design, development, support, deployment, and training. Understanding these phases is crucial for a successful implementation.
How long does an ERP implementation typically take?
ERP implementations typically take anywhere from six to twelve months, with a median timeline of about nine months for many businesses, thanks to the efficiencies of cloud and SaaS deployments.
What are the critical success factors for ERP implementations?
Successful ERP implementations rely on strong executive leadership support, effective change management, comprehensive employee training, and the use of external consultants to enhance expertise. Prioritizing these factors significantly increases the likelihood of a successful outcome.
What are the common pitfalls in ERP implementations?
ERP implementations often face common pitfalls, such as high costs and time-consuming implementation, integration challenges, and risks associated with a big-bang approach. Proactive planning and a focus on continuous improvement are essential to effectively mitigate these risks.
Why is adopting cloud-based ERP systems becoming more popular?
Adopting cloud-based ERP systems is becoming more popular primarily for their cost savings, improved operational efficiency, and scalability. Additionally, organizations are increasingly valuing the accessibility and rapid deployment these solutions offer.





